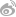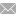Aristolochia tongbiguanensis, a new species of Aristolochiaceae from Yunnan, China

Aristolochia (Aristolochiaceae) is a family with about 550 species of lianas, shrubs, or tuberous herbs with peculiar zygomorphic flowers that are presumably adapted to fly pollination (Gonzalez, 2012). They grow mainly in tropical and subtropical regions with some species thriving in temperate regions (Kelly et al., 2003). In China, the genus Aristolochia has 61 species (Zhu et al., 2016, 2017). Aristolochia has three subgenera which are Siphisia, Pararistolochia and Aristolochia.
During a botanical expedition in Tongbiguan Provincial Nature Reserve, in SW Yunnan, the staffs from Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden (XTBG) collected an unknown species of Aristolochia.
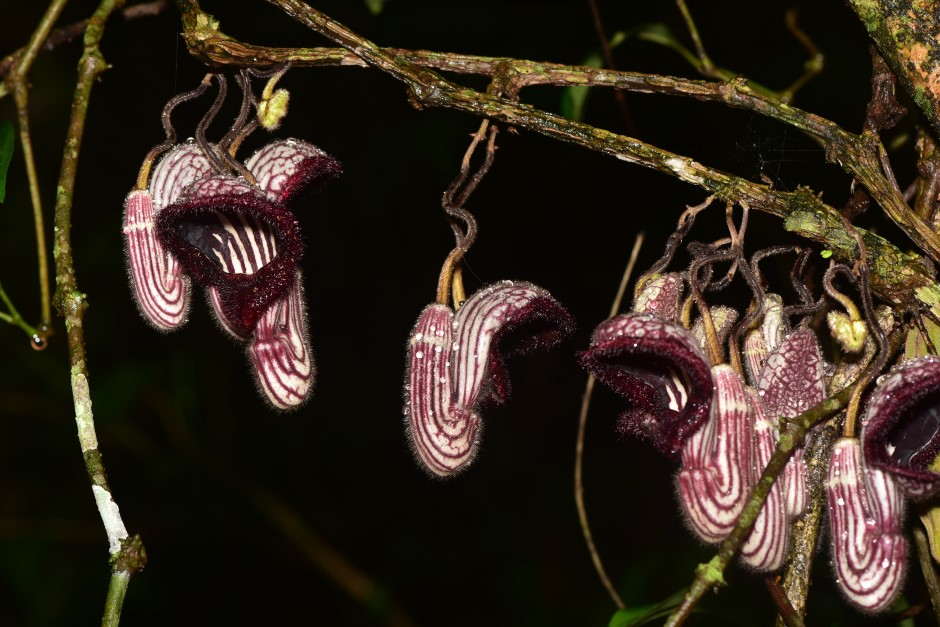
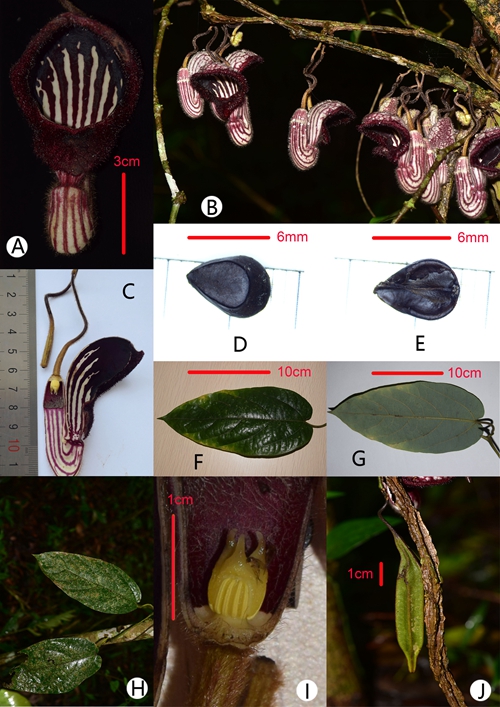
It is similar to A. tonkinensis, A. faviogonzalezii, A. balansae, A. saccata, and A. cathcartii, but the flower limb is nearly rectangular and covered with purple warts as well as long papillae and the throat is yellowish-white with dark purple lines and dots (see Figs. 1 & 2). After consulting national Floras and other relevant literature (Ma, 1989a, Ma, 1989b, Ma and Cheng, 1989, Do et al., 2015, Zhu et al., 2017) as well as numerous herbarium specimens, they made the conclusion that this is a new species.
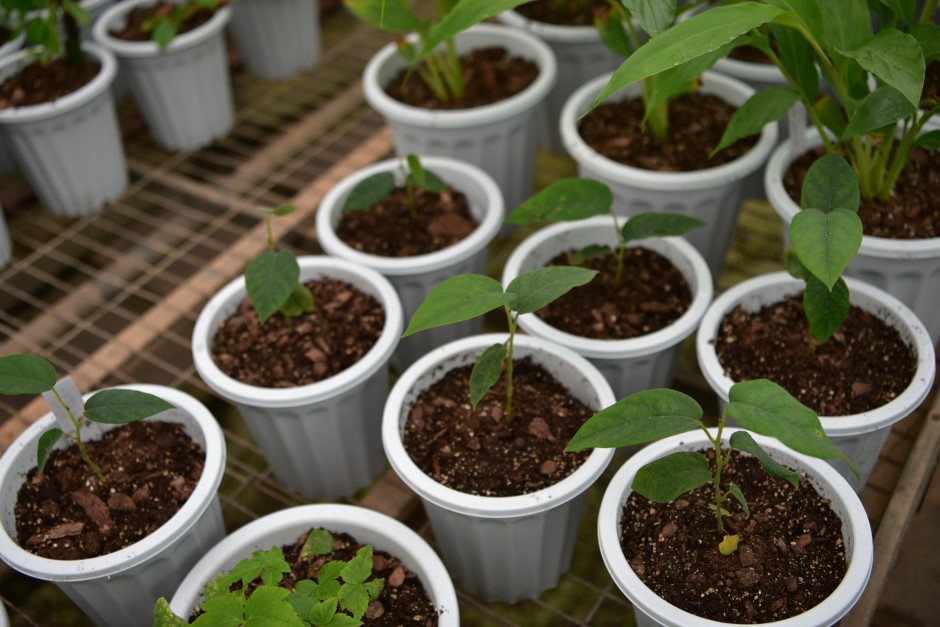
The Tongbiguan Provincial Natural Reserve was surveyed in September 2017 and three populations were found, each with less than three individuals. According to IUCN, this new species is assessed as Endangered (EN). Now XTBG has successfully bred 7 individuals through seed collecting
This study was supported by CUBG’s program “Full-Coverage Conservation Plan for Native Plants in China”, as well as the Investigation on medicinal plant resources of Dehong project (2017-17), the Conservation and application of National strategic tropical plant resources: theory and practice fund (2017XTBG-F05) and Science & Technology Basic Resources Investigation Program of China: Survey and Germplasm Conservation of Plant Species with Extremely Small Population in South-west China (2017FY100100).